Medieval Religion
During the medieval era, religion was incorporated in many people’s daily lives. These were the times when faith was strictly followed, there were crusades, pilgrimages, and exorcisms, and almost all men and women actually believed in heaven and hell. There were three faiths that people followed during those days in Europe: Judaism, Islam, and Christianity.
Judaism
Medieval Europe was a troubled time to live in for the Jewish. Many of them lived in Western Europe during 1000 and 1500 AD. During this era, two branches of Judaism emerged: the Sephardic centered in Spain and culturally linked with the Babylonian Jews; and the Ashkenazic, centered in France and Germany and linked with the Jewish culture of Palestine and Rome (history of Judaism).
The medieval Jewish philosophy and mysticism was that: God is creator, and there is only one god, (monotheism), that God is spiritual meaning non-physical. God is eternal. They believed in prayer unto one god alone, monolatry. They also had a strong belief in revelation/prophecy. Out of all the prophets they look at Moses as the most important prophet. They also believe that the Torah is law that is for all time. It was given to Moses, which showed the the importance of God’s commandments (Law). In Torah it says that God rewards those who follow God's Law and punishes those who transgress the law. God for them is omniscient (all knowing) of the hearts and minds of all people. They also believe that the messiah, a messenger of god will come. And there will be a resurrection of the dead (Medieval Judaism). In their little communities, their legal disputes were handled by rabbis and the rabbinical court .The Jewish followed the Torah and the Talmud very strictly. Therefore they abide by the dietary laws stated in the Torah, so in the communities, they provide the slaughter of cows, sheep, chicken, and goats in the prescribed manner. They also constructed and provided a bathhouse for the members to follow the rules of the ritualistic purification. Usually the communities that had a larger population sustained religious institutes where the Torah and the Talmud, the Jewish holy scriptures, are deeply studied, and also where they train rabbis (J. Kniesmeyer and D. Brecher 15).In succeeding generations, the study of the Talmud reached great heights. In Germany and Northern France, scholars known as the Tosafits utilized the method Talmudic interpretations (are interperters, mostly consist of rabbis who are part of the rabinical courts), and the Ashkenazic Jews composed religious poetry modeled on the liturgical (the rites for public worship) compositions, piyymtim, which is a Jewish liturgical poem.(Judaism, history belief, practice 154). With the forced conversions and expulsion from Portugal and Spain at the end of the 15th century, the highly developed communities of the Iberian Peninsula were destroyed and Sephardic Jews forced into renewed exile.Jews that migrated to Poland and Lithuania from the 13th century onward formed the basis of Russian Jews. Jews in Poland and Lithuania developed a particular mode of Talmudic study and enriched Jewish culture with many new religious streams and customs. Their religious academies attracted students from all over the Jewish world. They speak Yiddish, a mixture of medieval German and Hebrew (J. Kniesmeyer and D. Brecher 18).
The medieval Jewish philosophy and mysticism was that: God is creator, and there is only one god, (monotheism), that God is spiritual meaning non-physical. God is eternal. They believed in prayer unto one god alone, monolatry. They also had a strong belief in revelation/prophecy. Out of all the prophets they look at Moses as the most important prophet. They also believe that the Torah is law that is for all time. It was given to Moses, which showed the the importance of God’s commandments (Law). In Torah it says that God rewards those who follow God's Law and punishes those who transgress the law. God for them is omniscient (all knowing) of the hearts and minds of all people. They also believe that the messiah, a messenger of god will come. And there will be a resurrection of the dead (Medieval Judaism). In their little communities, their legal disputes were handled by rabbis and the rabbinical court .The Jewish followed the Torah and the Talmud very strictly. Therefore they abide by the dietary laws stated in the Torah, so in the communities, they provide the slaughter of cows, sheep, chicken, and goats in the prescribed manner. They also constructed and provided a bathhouse for the members to follow the rules of the ritualistic purification. Usually the communities that had a larger population sustained religious institutes where the Torah and the Talmud, the Jewish holy scriptures, are deeply studied, and also where they train rabbis (J. Kniesmeyer and D. Brecher 15).In succeeding generations, the study of the Talmud reached great heights. In Germany and Northern France, scholars known as the Tosafits utilized the method Talmudic interpretations (are interperters, mostly consist of rabbis who are part of the rabinical courts), and the Ashkenazic Jews composed religious poetry modeled on the liturgical (the rites for public worship) compositions, piyymtim, which is a Jewish liturgical poem.(Judaism, history belief, practice 154). With the forced conversions and expulsion from Portugal and Spain at the end of the 15th century, the highly developed communities of the Iberian Peninsula were destroyed and Sephardic Jews forced into renewed exile.Jews that migrated to Poland and Lithuania from the 13th century onward formed the basis of Russian Jews. Jews in Poland and Lithuania developed a particular mode of Talmudic study and enriched Jewish culture with many new religious streams and customs. Their religious academies attracted students from all over the Jewish world. They speak Yiddish, a mixture of medieval German and Hebrew (J. Kniesmeyer and D. Brecher 18).
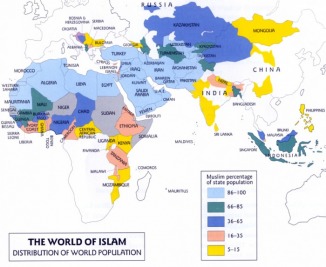
Islam
Islam was mainly dominant in Spain and Portugal during the medieval era. They resided there until they were driven out by war. Islam was closely related to Judaism and Christianity. Muslims believed that there was only one God, ‘Allah’. They believed that Moses and Jesus both existed, as well as the prophet Muhammad. Their holy scripture were called the Qur’an. Many of the stories in the Koran are the same as the stories in the Judeo-Christian Bible. They believed in a life here and hereafter, and if you pleased Allah, your life here and hereafter will be good. The way to please Allah would be to have no other gods except for Allah. Another way to please Allah would be to pray five times a day facing towards Mecca, the Muslim holy land, and to travel to Mecca sometime during your life.This journey was called the Hajj. Allah would have liked for his followers to give charity to the poor. And lastly he would have liked for his followers to fast, not eating during the day time, during the holy month of Ramadan.
On top of that, Allah forbade men or women to eat pork, drink alcohol, or to make pictures of people. Just like Christianity and Judaism, Islam didn’t have animal sacrifices, they only relied on prayer. However the Eid al-Adha was the only exception, it was the festival at the end of the Hajj when people would sacrifice a sheep. Just like medieval Judaism, Islam was also divided into two main kinds of Muslim’s during 650 AD. Most Muslims were Sunnis,Sunnis are considered the islamic orthodox and follow practices of the Prophet, Muhamed; nevertheless there were also a lot who were Shiites, Shiites believes Ali to be the true Prophet, not Muhamed. Sufism (a movement after the death of Muhamed) is another important part of early Islam. It was belief in a direct relationship between people and god. This belief is shared among many Sunnis and Shiites (History of Islam).
On top of that, Allah forbade men or women to eat pork, drink alcohol, or to make pictures of people. Just like Christianity and Judaism, Islam didn’t have animal sacrifices, they only relied on prayer. However the Eid al-Adha was the only exception, it was the festival at the end of the Hajj when people would sacrifice a sheep. Just like medieval Judaism, Islam was also divided into two main kinds of Muslim’s during 650 AD. Most Muslims were Sunnis,Sunnis are considered the islamic orthodox and follow practices of the Prophet, Muhamed; nevertheless there were also a lot who were Shiites, Shiites believes Ali to be the true Prophet, not Muhamed. Sufism (a movement after the death of Muhamed) is another important part of early Islam. It was belief in a direct relationship between people and god. This belief is shared among many Sunnis and Shiites (History of Islam).
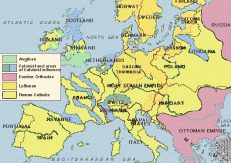
Christianity

When people think of the Middle Ages they think of a religious period, the time when the Christian church was the most important institution, and it was. There were other religions that existed during this time, but Christianity was the leading one. This was the time where great cathedrals were built all throughout Europe. And where there was no separation between church and state. There were two main types of Christianity, Orthodox, and Catholic (Medieval Religion). The Eastern Orthodox Church likes to think of itself as the original church with the Roman Catholic having split off from it. The Roman Catholic Church likes to think it is the original church with the Orthodox splitting away from Roman Catholic. Since they couldn't solve their differences,from 1054 onward, the two churches continued to develop in different directions, independent of each other. Christianity and Judaism are closely linked. Christian’s holy book is the Bible. They believe Jesus is the Messiah mentioned in the Hebrew text.Church dominated everybody's life. All Medieval people - village peasants or town's people - believed that God, Heaven and Hell all existed (The Medieval Church). Worship was held on Sundays and Christians celebrated Easter and Christmas.Sacraments of the Eucharist, Baptism and Confession were in practice, and with that Monastic communities began to develop; the first was the Benedictines which set the model of poverty, chastity and obedience coupled with prayer, work and service to those in need (Christianity). Many people believed that they could only go to heaven if everybody around them was a good Chrisitans too, so if you believed differently from them, you were forcing them to go to hell. Because of this Christians wanted everyone else to be Christians as well. They tried to get rid of the Jews by converting them or by driving them out. Sometimes Christians even led crusades against the Muslims residing in Spain. Pilgrimages were an important part of religious life in the middle ages. Many people took journeys to visit holy shrines such as the Canterbury Cathedral in England, as well as many others. (The Medieval Church)
Influence of Art, Literature and Architecture on Religion
Roman art, German Art , and Islamic Art mixed together in the the early Middle Ages to create a new form, which we call medieval art. First is Late Antique art, where some people made art in a more or less Roman style, so people would know they were Roman Christians. After Late Antique art came Romanesque art, where German, Roman, and Islamic elements mixed and brought a new energy and excitement to architecture sculpture and painting. This form of art was more abstract, combining stiff, formal forms in some places with fantastic carvings of real and imaginary animals and demons in others. Nearly all Romanesque art was of Christian themed.Romanesque art then turned into Gothic art around 1100 AD in Italy, and then spread slowly over Europe between 1100 and about 1300 AD. The easiest way to recognize Gothic architecture was by the pointed arches, but in general Gothic architecture shows a new ambition to reach higher and lighter, with walls of glass, reaching up to Heaven.Gothic sculpture showed more concern for realism than Romanesque, and more emotion. Now Mary appears everywhere, and Jesus becomes more merciful, compassionate, loving. In painting, artists also searched for more realism and more emotion. They began to experiment with backgrounds and crowd scenes.(Medieval Art). Architecture was infulenced by religion, in the way that they started to create building for religious gatherings. Such as the Synagogues, Mosques, and Churches.
This page was created by Bindiya Patel